Download Physical Characteristics Data Dictionary
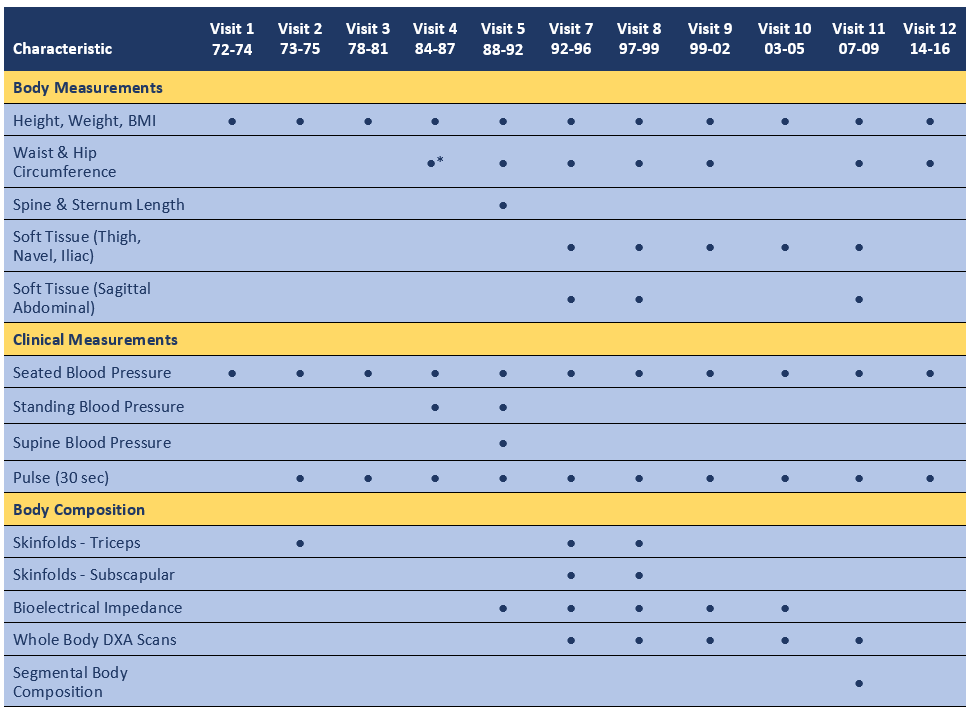
Physical characteristics such as height, weight and blood pressure were measured at every research clinic visit using standardized procedures and measuring devices. Whole body dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans were introduced at Visit 7 and obtained at all subsequent visits with the exception of Visit 12.
Body Measurements
Waist. Minimum waist circumference (the minimum waistline between the last rib and the superior iliac crest) and circumference at the bending point was measured in centimeters, to the nearest tenth. Note: minimum waist circumference was added to the protocol towards the end of Visit 4, so is only available on a subset of participants at this visit.
Hip. Circumference at the level of the superior iliac, at the greater trochanter area and at the maximum girth between the iliac crest and lowest area of the buttock was measured in centimeters, to the nearest tenth.
Sternum. Length from the tip of the manubrium to the tip of the xiphoid process was measured in centimeters, to the nearest tenth.
Spine. Length to the nearest tenth cm was measured between C7 (cervical bony prominence) to the bending point at the waist.
Thigh. Circumference, to the nearest tenth of a cm, was measured around the mid-thigh, half way between the inguinal crease and the proximal border of the patella. The measurement was done twice.
Blood Pressure Measurements
Blood Pressure: At each visit, systolic and diastolic blood pressures were measured in rested, seated participants. At all visits, except Visit 1, a second measurement was obtained 5 minutes later. Blood pressures were obtained according to the Hypertension Detection and Follow–Up Program Protocol, 1979. At Visit 4, standing blood pressure and post-phlebotomy seated blood pressures were obtained. At Visit 5, blood pressures were measured 1 minute after standing up, 3 minutes after standing up, and while lying supine. At all visits except Visit 12, blood pressures were measured with a standard mercury sphygmomanometer. At Visit 2, blood pressures were additionally measured with a random zero sphygmomanometer. At Visit 12, blood pressures were measured with the BP Tru Automated Blood Pressure Monitor.
Body Composition
Skinfolds. Skinfold thickness was measured in centimeters (cm) using Harpenden calipers applied to a fold of skin pinched between the thumb and index finger at a point where the sides of the skinfold were approximately parallel. Care was taken to ensure that only skin and adipose tissue were included in the fold. The subscapular skinfold was measured 1 cm inferior to the inferior angle of the scapula while the participant was standing with arms relaxed at the sides of the body. The triceps skinfold was measured at the midpoint between the acromial process and the inferior border of the olecranon process of the ulna, with the elbow flexed to 90 degrees. Each measurement was taken twice.
Bioelectrical Impedance. Measures of bioelectrical impedance were obtained from electrodes placed on the back of the hand and wrist, and top of the foot and ankle using the 1990A Bio-Resistance Body Composition Analyzer from Valhalla Scientific. Measures obtained include bio-resistance, total body fat, fat free mass, lean to fat ratio, total body water, and resting energy expenditure.
Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA). Whole body DXA scans were used to measure bone mineral content and appendicular and trunk fat and lean body mass at Visits 7 through 11. The Hologic 2000 was used for Visit 7, Visit 8, and Visit 9; the Hologic 4500 for Visit 10; and the Hologic Discovery W for Visit 11.
Segmental Body Composition. Measures of body fat and weight were obtained using the Tanita Body Composition Monitor (model BC-558) at Visit 11 only. These measures were not obtained on individuals with pacemakers or implanted metal materials (such as knee or hip replacements, or rods/pins for fractures) or on individuals who could not stand unaided. Obtained measures include percentage total body fat, and percentage fat in arms, legs, and trunk; total muscle mass and muscle mass in arms, legs and trunk; weight, percent body water, bone mass (in pounds), basal metabolic rate, metabolic age, and ratings of physique (based on ratio of fat to muscle, ranging from 1 – obese to 9 – very muscular) and visceral fat (ranging from 1-59; ratings below 13 are indicative of healthy levels of visceral fat).
