Download Pulmonary Function Data Dictionary
At Visits 5 and 11, participants completed a questionnaire on respiratory symptoms, conditions, medication use, and lung surgery, and underwent a pulmonary function test. Spirometry was performed by a trained technician using a water-sealed spirometer from Warren E. Collins, Eagle models, (Braintree, MA) at Visit 5; and an EasyOne Plus Spirometer from ndd Medical Technologies, Inc (Andover, MA) at Visit 11. Spirometers were calibrated daily and quality assurance measures were performed before and during the spirometry in accordance with the 1987 American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines. Participants performed from three to six tests to satisfy the ATS standards of acceptability and reproducibility. Results from the best attempt are provided.
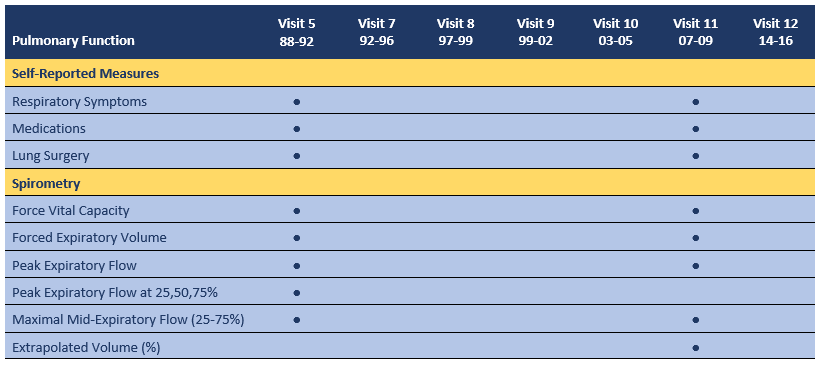
Self-Reported Measures
Participants were asked whether they experienced shortness of breath, wheezing, asthma, or hay fever, or if they ever had lung surgery. They were also asked whether they used inhaled medications or oral steroids.
In multiple visits (including Visits 5 and 11), participants were asked whether they had ever been diagnosed with pulmonary disease or asthma (see Health Status). Pulmonary disease was also queried in numerous mailers, and respiratory symptoms were queried in detail in Mailer 26 (2009).
Spirometry Measures
Forced vital capacity (FVC): the maximum volume of air, in liters, forcibly and rapidly exhaled after full inspiration.
Forced expiratory volume: the volume of air, in liters, expelled in the first second of a forced expiration (FEV1), and in the first 3 seconds (FEV3).
Peak expiratory flow (PEF): speed of the air moving out of the lungs at the beginning of the expiration, measured in liters per second.
Forced expiratory flow (FEF): rate of airflow at 25, 50, and 75% of the forced vital capacity, measured in liters per second.
Maximal mid-expiratory flow (MMEF): rate of airflow over the middle half (25% to 75%) of the forced vital capacity, measured in liters per second.
Extrapolated Volume (%). This measure is used to detect hesitation upon exhaling early in the test, and is calculated as % FVC. A value > 5% is considered unacceptable.
References
- Frette C, Barrett-Connor E, Clausen JL Effect of active and passive smoking on ventilatory function in elderly men and women. Am J Epidemiol. 1996; 143(8):757-65. PMID: 8610685.
- Lee HM, Liu MA, Barrett-Connor E, Wong ND. Association of lung function with coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease outcomes in elderly: the Rancho Bernardo Study. Respir Med. 2014;108(12):1779-85. PMID: 25448311; PMCID: PMC4254667
- American Thoracic Society. Standardization of spirometry; 1987 update. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987;136:1285-98.
