Overview
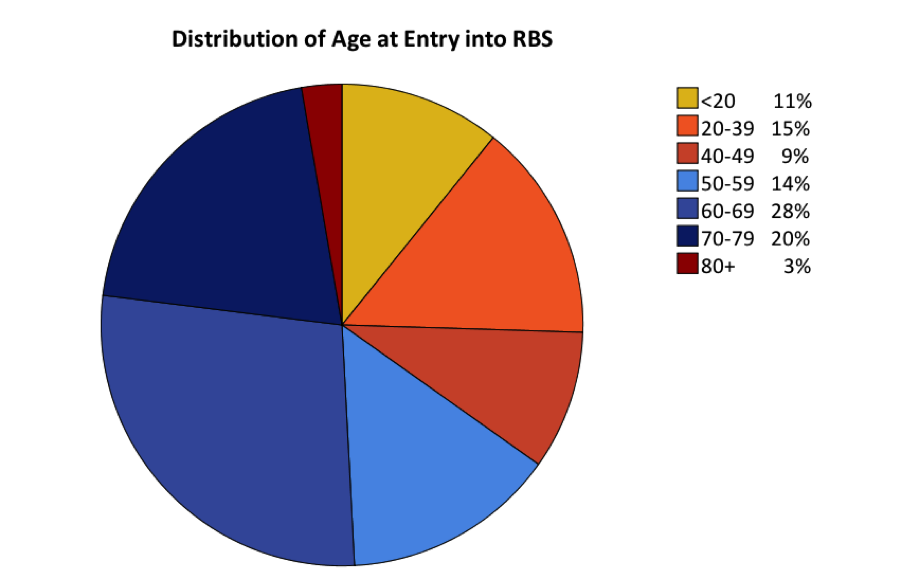
The Rancho Bernardo Study (RBS) of Healthy Aging began in 1972-74 as a population-based heart disease risk factor screening survey of all residents of the southern California community of Rancho Bernardo, a suburb of San Diego. The original study, including the first two research clinic visits, was part of the nation-wide Lipid Research Clinic (LRC) Prevalence program, a multi-centered collaborative study funded by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Subsequent RBS visits have been supported by grants from the National Institute of Aging (NIA), the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), the Agency for Healthcare Policy and Research (AHCPR), and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). The RBS archive includes data on 6726 participants; most (76%) were age 40 or older at the time of enrollment; 51% were age 60 and older. Overall, 94% of participants were enrolled in the RBS cohort at its inception in 1972-74 (Visit 1); the remaining 387 were recruited from the Rancho Bernardo community and enrolled at subsequent visits as detailed in the descriptions of each research clinic visit below. Each RBS participant was assigned a 9-digit subject ID code at entry into the cohort, which is used to link all participant data in the RBS Archive.
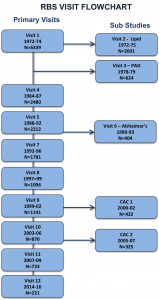
NOTE: Most RBS research clinic visits targeted initial or longitudinal assessment of one or more of the primary RBS outcomes of interest: cardiovascular disease, bone health, diabetes, cognitive function, physical function, health status and vital status. As shown in the RBS visit flow chart and noted in the individual visit descriptions, some research clinic visits were sub studies restricted to a select subset of RBS participants and a specific outcome.
PAD=peripheral arterial disease, CAC=coronary artery calcification